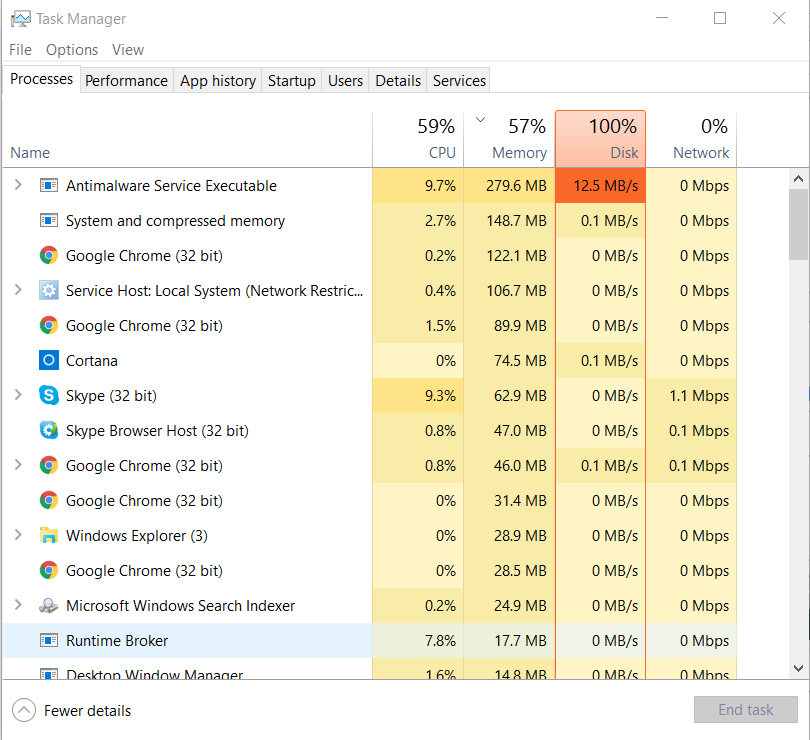
‘Antimalware Service executable’ causing a slow Windows 10/11? I can help!
The ‘Antimalware Service executable’, also known as Windows Defender, is crucial to your system’s security.
However, it can sometimes consume significant system resources, causing your PC to slow down. This guide offers a step-by-step approach to controlling this service, ensuring your computer runs smoothly without compromising security.
What is Antimalware Service Executable?
The Antimalware Service Executable process is associated with Microsoft’s Windows Defender, the built-in antivirus and security feature in Windows 10 and 11. The actual process is seen in the Task Manager as MsMpEng.exe.
This function is a core part of the Windows Defender service and can often be found running in the background of your operating system when analyzing your system for harmful software.
3 Roles of Antimalware Service Executable in Windows 10/11
Antimalware Service Executable plays a vital role in the Windows security infrastructure, with the following key responsibilities:
1. Real-Time Protection
The Antimalware Service Executable process allows for real-time monitoring of your system. It scans files, installations, and applications in real time, detecting and blocking malware as soon as it appears. This capability limits the potential for malware to run or spread on your computer.
2. System Scan
Apart from its real-time protection, the Antimalware Service Executable process is responsible for the periodic comprehensive system scans that Windows Defender performs. It checks every file on your system for potential threats and will quarantine or remove any harmful software detected.
3. Updates
The Antimalware Service Executable ensures that Windows Defender’s malware definitions are updated. This feature implies that Windows Defender stays current with the latest known threats and can effectively prevent these new forms of malware from compromising your system.
Every time you connect to the Internet and if updates are available, the Antimalware Service Executable will automatically download and install them.
Reasons to Stop Antimalware Service Executable

Here are a few such scenarios and potential problems they might cause:
1. High CPU Usage
At times, the Antimalware Service Executable can consume significant CPU resources when performing tasks like scanning, updating, or real-time monitoring.
This high CPU usage can lead to performance issues like slowdowns, lagging, or generally unresponsive behaviour of your computer. In such cases, temporarily stopping the service might help alleviate the problem.
2. Conflicting With Third-Party Antivirus Software
If you’re using an alternative antivirus software that conflicts with Windows Defender, you may need to disable the Antimalware Service Executable to avoid compatibility issues.
Running multiple antivirus programs simultaneously can cause system instability, performance problems, or undesired behaviour in the antivirus software itself.
3. False Positives
In some situations, the Antimalware Service Executable might flag legitimate software or processes as potentially harmful. These false positives can be disruptive, especially if they interfere with critical business applications, causing interruptions in your workflow.
Stopping the service can help resolve such issues until Windows Defender’s definitions have been updated or exclusions have been added for the mistakenly flagged applications.
4. Customized Security Setup
Advanced users with a tailored security setup might require complete control over their system’s protection mechanisms.
Disabling the Antimalware Service Executable might be necessary if the user knows the risks and prefers relying on other specialized software and methodologies to secure their system.
It’s important to note that stopping or disabling the Antimalware Service Executable should be considered a temporary measure, and users need to be aware of the potential security risks involved.
Always ensure your system is adequately protected against malware by re-enabling the Antimalware Service Executable or using an equally capable alternative.
Methods to Stop Antimalware Service Executable on Windows 10/11
Here are several methods to stop the Antimalware Service Executable:
Method 1 – Using Windows Security
Follow these steps to disable Antimalware Service Executable:
- Open the Start menu.
- Search for “Windows Security” and open it.
- Click on Virus & Threat Protection.
- Under “Virus & threat protection settings”, click on Manage settings.
- Toggle Real-Time Protection to off. This will stop the scan and, in effect, stop the Antimalware Service Executable.
Method 2 – Changing Windows Registry Settings
Warning: The registry is a sensitive part of your Windows system. Incorrect changes can cause serious system problems. Proceed at your own risk.
To disable Antimalware Service Executable through the registry:
- Press the Win + R key, then type regedit and hit Enter.
- Navigate to this directory: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender.
- If you find a key named DisableAntiSpyware, double-click it and set its DWORD value as 1.
- If you don’t find this key, right-click to create it: choose New > DWORD (32-bit) Value, and name it DisableAntiSpyware. Set its HashMap value as
1.
Method 3 – Using Task Scheduler
Another way is through the Task Scheduler. Follow these steps:
- Press the Win + R key, type in taskschd.msc, and hit Enter.
- In the navigation pane, follow this path: Task Scheduler Library > Microsoft > Windows > Windows Defender.
- In the middle pane, double-click on Windows Defender Scheduled Scan.
- In the new window, switch to the Conditions tab, uncheck all options, and click OK.
- Repeat step 4 for Windows Defender tasks such as Windows Defender Cache Maintenance, Windows Defender Cleanup, and Windows Defender Verification.
After completing these steps, Antimalware Service Executable should cease running. Remember, these are temporary solutions, and it’s always advisable to have real-time anti-malware protection running.
Only disable it if necessary. Also, be careful when handling the Windows Registry, as incorrect changes can lead to system errors.
Conclusion
In this article, I discussed the Antimalware Service Executable, a crucial part of the Windows Defender in Windows 10/11.
Despite its high CPU usage at times, its role in providing real-time protection, system scanning, and automatic updates to protect your system can’t be understated.
While disabling it can resolve specific issues, it does come with significant risks; high CPU utilization should be weighed against system security. If you decide to disable it, mitigate risks by using a trusted antivirus program, scanning regularly, downloading files wisely, and using a firewall.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can I disable the Antimalware Service Executable?Yes, you can disable it, but it’s generally not recommended unless you have a good reason, like high CPU usage. If you do, have another antivirus program and firewall protection.
- Why is Antimalware Service Executable so high on the CPU?The high CPU usage usually happens when Windows Defender runs a full scan or updates its definitions. It should return to normal after those tasks are completed. If it doesn’t, you might need to look into ways to manage its usage.
- What should I do if I’m experiencing high CPU usage due to the Antimalware Service Executable?You can schedule the scans when you’re less likely to feel the impact of slower performance or consider using a different antivirus program. Also, ensure that your files and programs are not infected by malware, which often leads to high resource consumption.