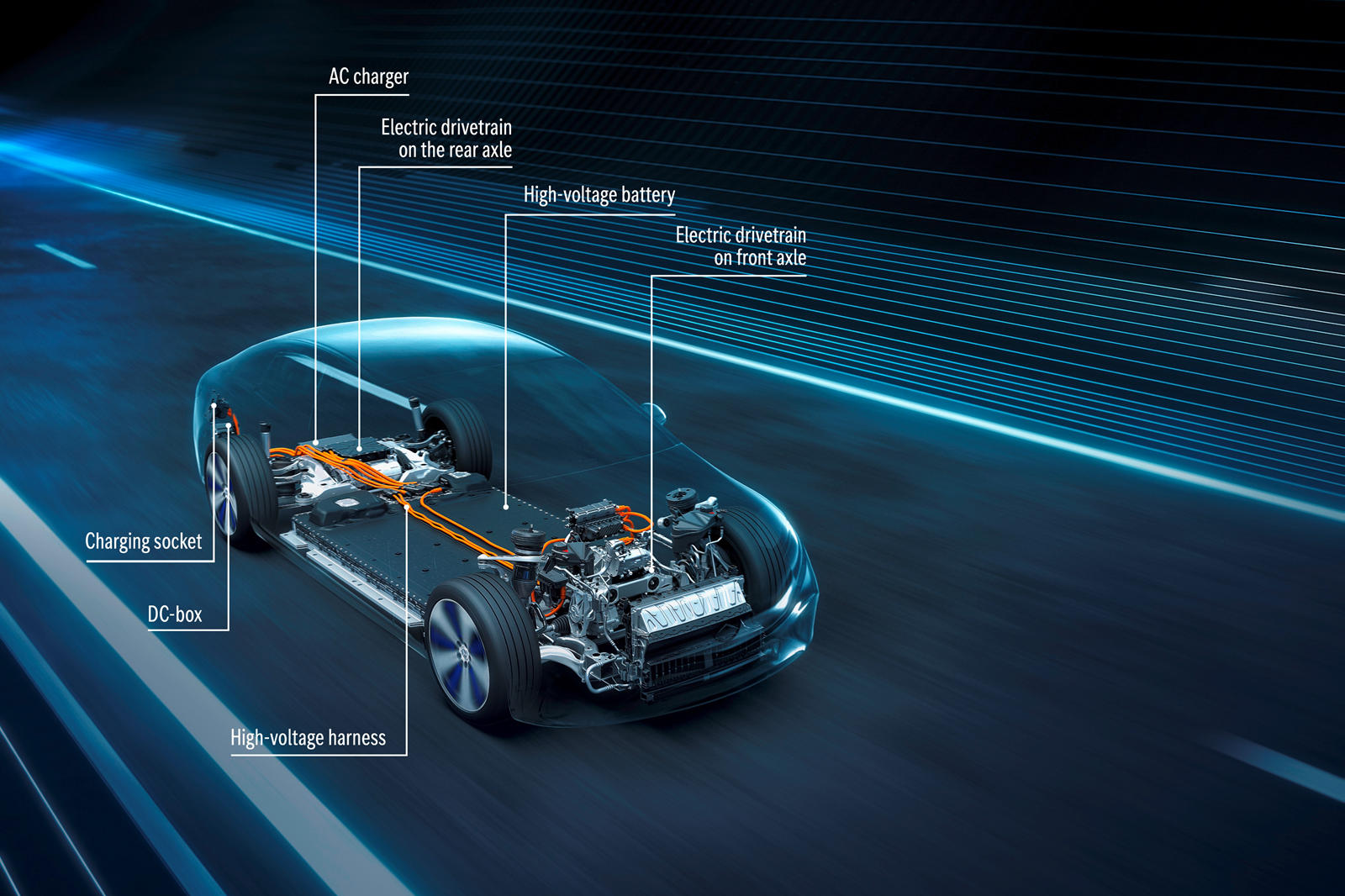
An electric vehicle is different from a gas-powered car in that it does not require a traditional engine to operate. Instead, it utilizes a battery pack and electric motor to travel along the roads.
An electric vehicle’s battery is responsible for storing the energy it receives from its charging station. This power is then transferred to the motor, which moves the wheels as well as charges the drivers’ mobile phones to play casino nz. Various electrical components work together to make the motion possible.
Key Components of an Electric Car
Understanding the various electrical components of an electric vehicle is very important to ensure that you have the best possible experience.
Charge Port
The electric vehicle’s charge port enables the car’s battery pack to receive power from an external source. This source, which is referred to as EVSE, is commonly referred to as a charging station’s equipment.
When an electric vehicle’s EVSE is connected to a charging port, it will start charging.
An EVSE that utilizes a 240-volt outlet can provide a car with enough power to recharge its battery.
Inverter
An electric vehicle’s battery pack is then converted into an AC by an inverter, which is a component that is required to power the car’s electric traction motor. Since lithium-ion batteries are only allowed to accept DC power, an electric vehicle’s traction motors need AC power to function. Besides controlling the AC power that is sent to the motor, an inverter also plays a vital role in controlling the vehicle’s speed.
Electric Traction Motor
The electric traction motor turns a car around by moving the wheels using the power it receives from the electricity it receives from the inverter. This type of motor is more reliable and efficient than a DC motor. The electrons from the AC source that are sent to the motor through the inverter generate a magnetic field, which then causes it to turn.
An electric traction motor is powerful and efficient because it doesn’t have a variety of gears. This makes it ideal for use in cars that require immediate power from the pedal.
Traction Battery Pack
The electric vehicle’s traction battery pack is primarily responsible for storing the energy that’s collected from the grid when it’s charging. This energy is used to power the motor and other electrical components.
Most electric cars on the market today feature a lithium-ion battery pack, which is one of the most energy-dense types of batteries. Compared to other types of batteries, this type of pack produces larger currents and requires less maintenance. Some cars also have an auxiliary battery that’s designed to power the vehicle’s accessories.
Electric Powertrain
The electric vehicle’s powertrain includes the high-voltage electrical components needed to operate the car. These include an inverter, a reduction drive, and a traction motor.
The electric powertrains of modern cars are compact, lightweight, and provide quick torque. They can also recover lost energy during deceleration. Regeneration is a process that involves converting unused AC power into DC power.
Types of Electric Cars
Most electric cars are designed by modern car companies to provide their customers with various benefits and features.
Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV)
A battery-only vehicle is known as a BEV. Unlike traditional cars, which use internal combustion engines, this type of vehicle does not emit harmful tailpipe emissions. It’s powered by a battery pack and receives all the electricity it requires from the grid through EVSEs.
Hybrid Electric Vehicles (HEV)
HEVs are low-emission vehicles that utilize a small battery pack in order to assist a traditional internal combustion engine. Since they don’t have a plug-in, they rely on a generator and regenerative braking to recharge their batteries.
Even though HEVs can’t solely rely on electric power, they can still achieve an impressive fuel economy by using a lower-powered gasoline engine.
Plug-In Hybrid Vehicles (PHEV)
A plug-in hybrid vehicle has an internal combustion engine and a traction motor. This means that it requires gasoline and EVSE to operate. The vehicle’s battery pack will run out of power at some point, so it will continue running on electricity until its engine turns on.