Are you curious about the best graphics option between PEG and IGD? Here, I’ll break down the differences between the two leading choices, PEG (PCI Express Graphics) and IGD (Integrated Graphics Device).
From gamers to normal users, I’ll cover everything as we compare these two major graphics solutions.
Want to choose wisely between PEG and IGD for your computer? Stay tuned for this head-to-head breakdown.
PEG and IGD: A Basic Overview
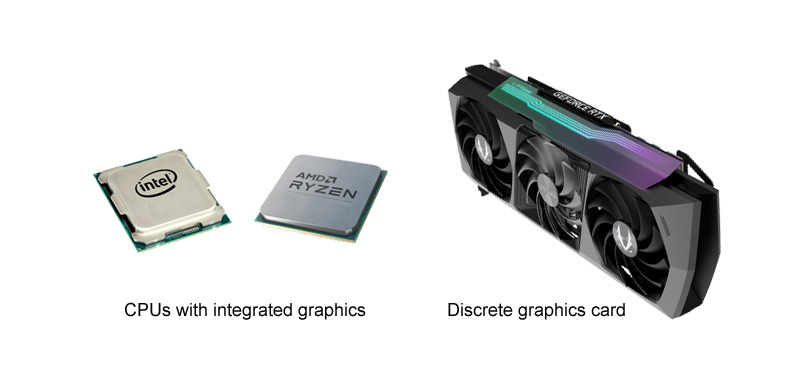
So what are PEG and IGD, you may ask? To understand the fundamental differences between the two, let’s explore their overview:
- PEG (PCI Express Graphics): As a successor to the PCI and AGP standards, PEG is a high-speed, serial computer expansion bus primarily used for graphics cards. It’s especially favorable in executing graphic-intensive games and software applications that require a robust Graphics Processing Unit (GPU).
- IGD (Integrated Graphics Device): IGD is a graphics capability set directly into the system’s motherboard or CPU. Although IGD lacks the high-performance capabilities of dedicated GPUs, it offers benefits like energy efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and adequate performance for standard everyday computing tasks.
Technical Specifications of PEG and IGD
Now let’s dive deeper into the technical specifications, presenting distinct comparisons between PEG and IGD:
- Hardware Compatibility: While PEG utilizes a PCIe slot, usually in x16, x8, or x4 forms on the system’s motherboard, IGDs are integrated directly into the computer’s CPU or chipset. This means that no additional slots are required for IGDs.
- Software Requirements: Here’s something important – PEG and IGD have different software and driver requirements that cater to their functionalities. Like any software, regular updates and patches are needed to counter bugs and keep the systems running effectively.
- Performance Characteristic: PEG definitely takes the lead when it comes to handling demanding graphical operations, thanks to its dedicated VRAM and robust processing capabilities. However, don’t underestimate IGD performance for everyday computing tasks. There have been significant improvements in recent years!
PEG vs IGD: Performance Benchmarks
Can numbers help to identify which is faster or more efficient? Performance benchmarking provides such valuable, quantifiable data:
- With its dedicated VRAM and robust processing capabilities, PEG generally outperforms IGD in graphics-heavy workloads such as professional gaming, 3D rendering, or high-definition video editing.
- On the other side of the spectrum, IGD has stepped up its game over the years, confidently handling everyday computing tasks. Remember that it may lag when dealing with high-end games or resource-intensive graphical processing.
PEG vs IGD: Cost-effectiveness
How about costs? The cost is always an important dimension in any comparison:
- PEG GPUs come attached with extra expenditure – both upfront during the purchase and over time due to increased power consumption.
- IGD, although not delivering the high-end performance of dedicated graphics cards, comes bundled with your CPU. This means no extra spending and lower power bills over time.
PEG vs IGD: Security
You must be interested in security, correct? Examining security vulnerabilities and features should always be on top of your checklist:
- While PEG and IGD offer standard security protocols, potential vulnerabilities can arise. To overcome these risks, it’s essential to perform regular driver and firmware updates to patch any existing security loopholes and maintain secure environmental conditions.
PEG vs IGD: Compatibility

What about compatibility issues? It is vital to consider how each option fares with various hardware, software, and operating systems:
- Compatibility with PEG graphics cards is broad-ranged. However, it depends significantly on the specific GPU and the extent of support its manufacturer provides.
- IGD displays more consistently compatible performance across systems since most CPU driver support packages include support for integrated graphics.
PEG vs IGD: Scalability
Are you thinking about the future? Scalability becomes a decisive point when looking ahead:
- The advantage of tipping towards PEG lies in the capacity to upgrade the GPU in the future by swapping the graphics card on the motherboard. This flexibility assures greater scalability, allowing users to stay in tune with contemporary graphics requirements.
- Unfortunately, IGD offers limited room for upgrades, given that graphics are integrated into the motherboard or the CPU.
My Experience with PEG and IGD
Now, before I end this post, let me share my experience with PEG and IGD –
- Installation and Interface: PEG is an external component that needs to be installed into the PCIe slot, followed by driver installation and configuration. For newbies, the process might seem intimidating. IGD, on the other hand, comes as part of the CPU architecture, making it a popular choice for casual technology users.
- Common Issues and Complaints: When it comes to issues with PEG and IGD, the biggest grievance I’ve is power efficiency. PEG systems consume more power and run hot, while IGD systems excel in power efficiency but struggle during resource-intensive tasks.
Parting Thoughts
So, which one is right for you? PEG is great for heavy tasks like gaming and professional use, while IGD excels in everyday tasks.
But in the end, recognizing whether your needs align with the everyday computing tasks suited for IGD or the high-performance tasks suited for PEG helps guide your decision-making process.
And here’s the best part: the computing world is always evolving!
Both PEG and IGD will continue to bring notable developments to the world of computer graphics as developers seek innovations to boost their performances.
And when that happens, I’ll let you know about them.



